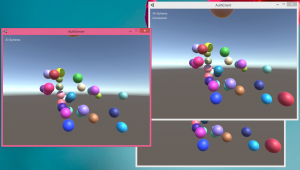
An authoritative server in my mind is where the clients send their key presses to the server, and the server tells the clients where their character is located. This example here is kind of like a “Hello World”, or rather just a “Hello”, if that, because I don’t have the clients sending anything to the server. The server will generate spheres and then send the sphere positions to any clients connected and the clients display the spheres for the user. Here you can see a server with two clients connected.
Now keep in mind I have no professional experience doing any of this and I don’t even know if this is the correct approach to take, but I’ve found very few examples of this kind of thing on the Internet (using Unity’s NetworkTransport). If you don’t know about NetworkTransport, read Checking out Unity’s NetworkTransport first. This does not use Unity’s High Level API because I wanted to have as much control as possible over what was sent on the network.
Let’s start. So let’s have the server spawn a sphere and add it to a list so we can keep track of everything:
IEnumerator SpawnCoroutine()
{
// Create new object
GameObject sphere = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Sphere);
sphere.AddComponent<Rigidbody>();
//sphere.GetComponent<Rigidbody>().velocity = new Vector3(UnityEngine.Random.Range(-1.0f, 1.0f), UnityEngine.Random.Range(-1.0f, 1.0f), UnityEngine.Random.Range(-1.0f, 1.0f));
// Set position
sphere.transform.position = new Vector3(UnityEngine.Random.Range(-2.0f, 2.0f), UnityEngine.Random.Range(-2.0f, 2.0f), UnityEngine.Random.Range(-2.0f, 2.0f));
// Set color
sphere.GetComponent<Renderer>().material.color = new Color(UnityEngine.Random.value, UnityEngine.Random.value, UnityEngine.Random.value);
// Save data for when we send across the net
sphereList.Add(sphere);
yield return new WaitForSeconds(5.0f);
sphereList.Remove(sphere);
Destroy(sphere);
}
Now we need another coroutine that runs every tenth of a second and sends the sphere list out to every connected client. A major complication is turning a List into a byte stream. Let’s first serialize the data:
// Serialize list
NetworkWriter nw = new NetworkWriter();
Renderer rend;
foreach (var item in sphereList)
{
nw.Write(item.GetInstanceID());
nw.Write(item.transform.position);
rend = item.GetComponent<Renderer>();
nw.Write(rend.material.color.r);
nw.Write(rend.material.color.g);
nw.Write(rend.material.color.b);
// Don't pack too much
// Fix me! Send more than one packet instead
if (nw.Position > 1300)
break;
}
// Send data out
byte[] buffer = nw.ToArray();
byte error;
//Debug.Log(string.Format("Sending data size {0}", buffer.Length));
foreach (var item in connectList)
{
NetworkTransport.Send(m_hostId, item, reliableChannel, buffer, buffer.Length, out error);
}
One shortcoming in this example is the server only sends the first 50 or so spheres out. We’d need to send more than one packet if we wanted more. NetworkTransport message size is limited as it’s UDP. I wrote the client so that it can handle different packets of spheres though. I’m going to use the GetInstanceID as a “primary key” for each sphere so we know if a client has the sphere yet or not.
Now here’s how the client will deserialize:
struct NetworkData
{
public int id;
public Vector3 pos;
public float r;
public float g;
public float b;
}
NetworkReader nr = new NetworkReader(buffer);
List<NetworkData> tmpList = new List<NetworkData>();
NetworkData tmpData;
// Read to the end
while (nr.Position != buffer.Length)
{
// Deserialize
tmpData.id = nr.ReadInt32();
tmpData.pos = nr.ReadVector3();
tmpData.r = nr.ReadSingle();
tmpData.g = nr.ReadSingle();
tmpData.b = nr.ReadSingle();
tmpList.Add(tmpData);
}
How does the client then turn this list into game objects? It remembers what game objects it’s already spawned.
class SphereData
{
public int id;
public float lastUpdate;
public GameObject obj;
}
// Remeber all spheres we spawned
List<SphereData> sphereList = new List<SphereData>();
Now we just take the List we deserialized earlier on the client and turn it into new spheres if we don’t have the game object already, or update the old sphere’s position:
SphereData sd;
foreach (var networkData in tmpList)
{
sd = sphereList.FirstOrDefault(item => item.id == networkData.id);
// Do we have this sphere already?
if (sd != null)
{
// Update position
sd.obj.transform.position = networkData.pos;
sd.lastUpdate = Time.realtimeSinceStartup;
}
else
{
// Create new object
GameObject sphere = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Sphere);
// No rigidbody here!
// Set position
sphere.transform.position = networkData.pos;
// Set color
sphere.GetComponent<Renderer>().material.color = new Color(networkData.r, networkData.g, networkData.b);
sd = new SphereData();
sd.id = networkData.id;
sd.obj = sphere;
sd.lastUpdate = Time.realtimeSinceStartup;
sphereList.Add(sd);
}
}
The client will delete spheres it hasn’t gotten info from the server about if enough time passes.
void CleanupSpheres()
{
foreach (var item in sphereList)
{
// Haven't heard about sphere in a while so destroy it
if (item.obj.gameObject != null && item.lastUpdate + 1.0f < Time.realtimeSinceStartup)
Destroy(item.obj.gameObject); // Note this becomes null only after Update
}
}
So there are two main scripts, Server.cs and Client.cs. I attach these to a Main Camera in their own separate projects.
Note you need to add a Sphere to the scene, but you can turn off the Sphere Collider and Mesh Renderer. This is to make it so Unity builds with the correct shaders needed for when you do spawn the spheres. Otherwise you will see pink spheres!
Also note pressing space on the server will cause a lot of Spheres to be generated.
In the future I hope to figure out a way to send more than 50 spheres to the clients, to get some interpolation going (a la what Gabriel Gambetta talks about), and eventually have clients moving the spheres around with them sending input. (It is also better to have the server send the sphere colors only once when they are created and not on each update!)
Both projects at GitHub